In the bustling world of electronics, metal stamping has emerged as a cornerstone fabrication technique. Its ascent underscores a commitment to precision and efficiency, reshaping how components are crafted. Did you know? The global electronics sector has seen a 20% surge in metal stamping adoption in the last five years.
Metal stamping harnesses the power of dies and presses, delivering unmatched precision and adaptability. This method stands out for its cost-effectiveness, setting new standards in electronics component production.
Join us as we journey through the expansive landscape of metal stamping, exploring its myriad benefits, inherent challenges, and the exciting horizons it promises in the electronics industry.

Enhanced Precision and Consistency
In the intricate realm of electronics, accuracy isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Every microchip, circuit board, or connector hinges on the precision of its components. A slight deviation can lead to malfunctions, compromising the entire device’s functionality. This is where metal stamping shines. By ensuring each component is crafted with meticulous precision, it guarantees the reliability and consistency that electronics demand.
But not all materials are created equal. For electronics, metals like copper, brass, and phosphor bronze are often favored. These materials not only offer excellent conductivity but also possess the malleability required for precise stamping. Their resilience ensures that the stamped components can withstand the rigors of electronic operations without degradation.
By embracing the precision offered by metal stamping and choosing the right materials, the electronics industry is poised to create devices that are more reliable than ever before.

Cost-Effectiveness in Mass Production
The electronics industry, with its ever-growing demand, requires production methods that are not only precise but also economically viable. Metal stamping stands out as a beacon of cost-effectiveness, especially when it comes to mass production. Here’s why:
Economic Advantages in Large-Scale Production:
The beauty of metal stamping lies in its scalability. Once the dies are crafted, they can be used to produce a vast number of components without significant wear and tear. This means that the cost per unit decreases substantially as production volume increases, offering economies of scale that few other methods can match.
Initial Investment:
While setting up a metal stamping operation might require a substantial initial investment, primarily in crafting the dies and procuring presses, the long-term benefits outweigh these costs. Given the durability of the equipment and the high production rate, the return on investment is rapid.
Maintenance and Operational Costs:
Metal stamping equipment is robust and designed for longevity. Regular maintenance costs are relatively low, and because of the efficiency of the process, operational costs, including labor and energy, are optimized. When compared to other fabrication methods that might require frequent tool replacements or more manual oversight, metal stamping proves to be more economical.
In the grand scheme of electronics manufacturing, metal stamping emerges as a frontrunner, offering a blend of precision and cost-effectiveness that’s hard to beat. As manufacturers aim to produce more while keeping costs in check, metal stamping presents a compelling solution.

Scalability and Versatility
The world of electronics is vast and varied, with components ranging from the minuscule to the massive. For a production method to truly shine in this industry, it needs to be both scalable and versatile. Metal stamping fits this bill perfectly.
Adaptability for Diverse Components:
Metal stamping’s true strength lies in its adaptability. Whether it’s a tiny connector for a smartphone or a larger component for an industrial machine, the same stamping setup can be tweaked to produce a wide range of parts. This flexibility means manufacturers can quickly shift between projects without the need for extensive tool changes or setup modifications.
Training and Skillset:
While metal stamping machines handle the bulk of the work, the human touch is indispensable. Professionals in this domain require a keen understanding of metals, dies, and the stamping process. They need to be adept at setting up the machines, ensuring the precision of each stamp, and troubleshooting any issues. Fortunately, with the right training programs, individuals can be equipped with the necessary skills to excel in this field. The industry has seen a rise in specialized courses and workshops, ensuring a steady stream of skilled professionals.
In conclusion, metal stamping’s scalability and versatility make it an invaluable asset in the electronics industry. Its ability to cater to diverse needs, combined with the expertise of trained professionals, ensures that the industry can meet the ever-evolving demands of the modern world.

Broader Implications:Global Perspective and Market Dynamics
The electronics industry, a truly global behemoth, has seen metal stamping play an increasingly pivotal role in its growth. However, the adoption and nuances of metal stamping can vary significantly across regions, influenced by local market dynamics, technological advancements, and economic factors.
Variations Across Regions
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): Dominated by manufacturing powerhouses like China, South Korea, and Japan, the APAC region has seen a rapid adoption of metal stamping. China, being a major electronics production hub, drives much of this demand. The availability of raw materials and skilled labor, combined with favorable government policies, has made this region a hotspot for metal stamping in electronics.
- North America: With a focus on high-quality production and advanced technologies, North American manufacturers often employ metal stamping for specialized, high-end electronic components. The region also sees a significant amount of R&D in stamping technologies, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
- Europe: European manufacturers, known for their emphasis on sustainability and precision, often integrate eco-friendly practices in their metal stamping processes. The region, with its stringent quality standards, ensures that stamped electronic components are both durable and environmentally friendly.
- Latin America & Africa: These regions, while still developing in terms of electronics manufacturing, are witnessing a growing interest in metal stamping, driven by increasing local demand for electronics and foreign investments in manufacturing sectors.
Evolving Market for Metal-Stamped Electronic Components
The global demand for electronics is insatiable, and with technological advancements, devices are becoming more compact and sophisticated. This trend necessitates components that are precise, reliable, and consistent—qualities inherent to metal stamping. As a result, the market for metal-stamped electronic components is on an upward trajectory.
Furthermore, as industries like automotive, aerospace, and healthcare increasingly integrate electronics into their products, the demand for stamped components expands beyond traditional electronics manufacturers.
Another notable trend is the push towards sustainability. With environmental concerns taking center stage, manufacturers are exploring ways to make metal stamping more eco-friendly, from using sustainable materials to recycling and waste reduction.
In conclusion, the global landscape of metal stamping in electronics is dynamic and influenced by a myriad of factors. From regional variations to evolving market demands, metal stamping remains at the heart of the electronics manufacturing revolution.
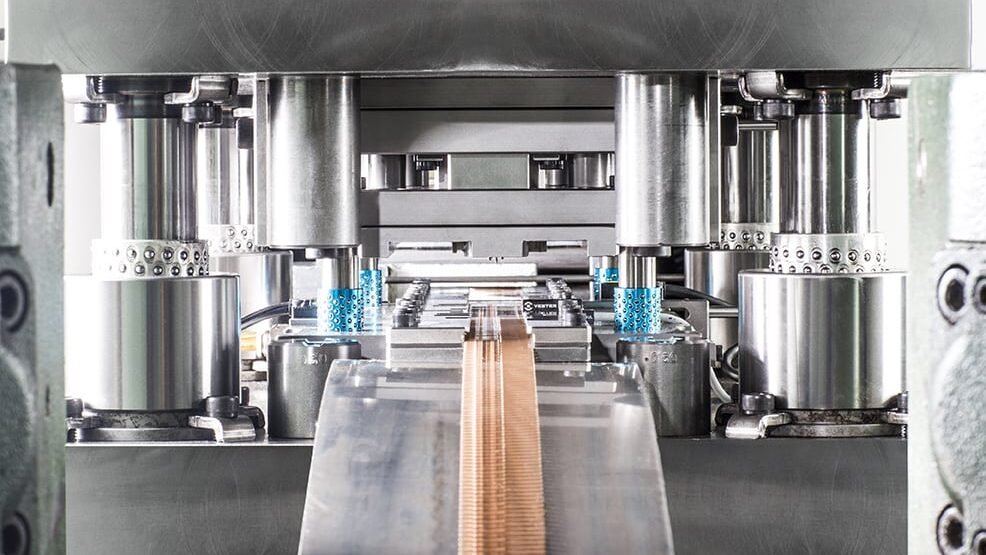

Broader Implications:Innovations and Competing Technologies
The realm of metal stamping, like many other manufacturing sectors, is in a constant state of evolution, driven by technological advancements and the quest for efficiency. As the electronics industry demands more precision and versatility, metal stamping has had to adapt and innovate.
Latest Technological Advancements in Metal Stamping
- High-Speed Stamping: With the need for faster production rates, high-speed stamping machines have been developed. These machines can produce stamped components at incredible speeds without compromising on precision.
- 3D Metal Stamping: Leveraging the principles of 3D printing, 3D metal stamping allows for the creation of more complex and intricate shapes, expanding the range of possible electronic components that can be produced.
- Smart Stamping: Integrating IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) into stamping machines allows for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of the stamping process, ensuring higher yields and reduced wastage.
- Precision Micro Stamping: As electronics become more compact, there’s a need for smaller components. Precision micro stamping focuses on producing tiny yet accurate parts essential for modern electronic devices.
Emerging Technologies Challenging or Complementing Metal Stamping
- Additive Manufacturing: Often known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing builds components layer by layer. While it offers the advantage of creating highly customized parts, its current speed and scalability might not match that of metal stamping for mass production.
- Laser Cutting and Engraving: For certain electronic components, laser technologies offer a high degree of precision. They can be used to cut or engrave intricate designs, especially for components that might be challenging for traditional stamping.
- Electrochemical Machining (ECM): ECM is a method where metal parts are machined through controlled anodic dissolution. It’s especially useful for producing complex shapes and surfaces in electronic components.
- Hydroforming: This method uses pressurized fluid to shape metal sheets into desired forms. It’s particularly effective for creating non-uniform shapes and might be used in conjunction with metal stamping for specific electronic components.
In conclusion, while metal stamping remains a dominant force in the production of electronic components, it’s clear that the landscape is evolving. Innovations within the domain ensure it stays relevant, while emerging technologies present both challenges and opportunities for integration and collaboration. The future of electronics manufacturing will likely see a blend of these techniques, each chosen for its unique strengths and advantages.
Conclusion
Metal stamping stands as a beacon of innovation in electronics, offering precision, cost-efficiency, and adaptability. Its multifaceted benefits have reshaped manufacturing, but the journey doesn’t end here. As technology advances, the onus is on us to continually explore and innovate, ensuring metal stamping’s enduring relevance in the ever-evolving electronics landscape.




One Response
I like that you mentioned how conventional metal stamping stands out due to its cost-effectiveness. I was checking out some production methods earlier and I learned about the use of metal stamping. It sounds pretty fascinating, so I am now trying to learn more about how it works.