Navigating the lead time for precision micro stamped parts is a nuanced journey, with each phase holding its significance. This guide elucidates the step-by-step ordering process, shedding light on the timeline from initial communication to the shipping of mass-produced parts, aiding in setting realistic expectations and ensuring a smooth manufacturing journey.
The ideal lead time for precision micro stamped parts encompasses various phases including OEM & ODM Communication (1-3 days), Tool & Die Design (3-7 days), Stamping Die Manufacturing (10-14 days), FOT Sample (3-7 days), Mass Production (20-30 days), and Booking & Shipping (7-10 days), aggregating to a comprehensive lead time spanning from 44 to 71 days.
Dive deeper into each phase, uncovering the intricacies that dictate the duration and exploring how effective communication and proficient execution contribute to adhering to the estimated lead time.

OEM & ODM Communication: Laying the Groundwork (1-3 Days)
In the realm of manufacturing precision micro stamped parts, the initial dialogue between the clients and the manufacturers forms the bedrock upon which the entire project rests. This phase, titled OEM & ODM Communication, is where the groundwork is laid for what is to unfold over the coming weeks. It is where ideas are shared, specifications are discussed, and a shared vision is cultivated. Here’s a closer look at this critical phase, broken down into its core components:
Understanding Client Needs:
The first step in this phase is understanding the client’s needs. This involves a detailed discussion regarding the specifications of the micro stamped parts – the materials, dimensions, tolerances, and any unique features that need to be incorporated. It’s a deep dive into the nitty-gritty of what the client needs and expects from the final product.
Clarification and Queries:
At this stage, after initial specifications are provided, manufacturers can ask questions or seek clarifications to eliminate any uncertainties. It’s essential to resolve ambiguities to ensure a mutual, clear grasp of the project needs. This may include exchanging detailed drawings, prototypes, or other documentation to fully comprehend the project’s scope.
Establishing a Communication Channel:
Creating a strong communication channel is key during this phase, maintaining an open line of information between clients and manufacturers. This enables regular updates, clarifications, or changes to project specifications, keeping all parties aligned.
Setting Expectations:
Lastly, this phase involves setting the right expectations regarding the lead time, costs, and other critical aspects of the project. It’s about aligning the expectations of the client with the capabilities and timelines of the manufacturer.
Finalizing the Agreement:
Post all discussions and clarifications, a formal agreement is made which outlines all the project details including the costs, timelines, and any other terms and conditions. This agreement serves as a reference point throughout the manufacturing process.
The OEM & ODM Communication phase, though brief, is densely packed with discussions, clarifications, and agreements that set the tone for the rest of the project. It’s a phase where clarity is sought, expectations are set, and a roadmap for the project is carved out, making it a pivotal step in the lead time journey of manufacturing precision micro stamped parts.

Tool & Die Design: Crafting the Blueprint (3-7 Days)
The process of crafting precision micro stamped parts is akin to creating a masterpiece; the essence lies in the blueprint. The Tool & Die Design phase is where imagination meets the paper, setting a solid foundation for the actual manufacturing process. This segment, which lasts between 3 to 7 days, is rife with creativity, precision, and meticulous attention to detail. Let’s dissect the crucial aspects that constitute this phase:
Understanding the Specifications:
Before diving into the design, a thorough understanding of the project specifications garnered during the OEM & ODM Communication phase is revisited. This ensures that the design team has a clear grasp of what needs to be achieved.
Initial Design Drafting:
Armed with the project specs, the design engineers embark on creating the initial drafts of the tools and dies. This involves leveraging advanced design software to create detailed blueprints that adhere to the specified dimensions, tolerances, and other critical parameters.
Material Selection:
The selection of materials for the tools and dies is a decision of paramount importance. The chosen materials need to withstand the rigors of the stamping process while ensuring the precision and quality of the micro stamped parts. Material selection is done based on the project requirements and the properties needed for the tools and dies.
Simulation and Analysis:
With the initial designs in place, simulation tools are employed to analyze the performance of the designed tools and dies. This virtual testing ground helps in identifying any potential issues or areas of improvement before moving to the manufacturing phase.
Design Revisions:
Based on the insights garnered from the simulation and analysis, revisions are made to the design to optimize it further. This iterative process continues until the design engineers are satisfied that the design will yield the desired outcomes.
Finalization and Approval:
Once the design is honed to perfection, it is subjected to a stringent review and approval process. This involves cross-verification with the project specifications and possibly a review with the client to ensure that the design meets the expectations and is ready to move to the next phase.
Documentation:
Post-approval, detailed documentation is prepared that encompasses all aspects of the design. This documentation serves as a reference during the Stamping Die Manufacturing phase, ensuring that the transition from design to manufacturing is seamless.
The Tool & Die Design phase is where the vision for the precision micro stamped parts starts taking a tangible form. It’s a phase that demands a blend of technical prowess, creativity, and a relentless pursuit for precision and quality. The designs crafted during this phase are the blueprints that guide the manufacturing process, making it a cornerstone for the success of the project.
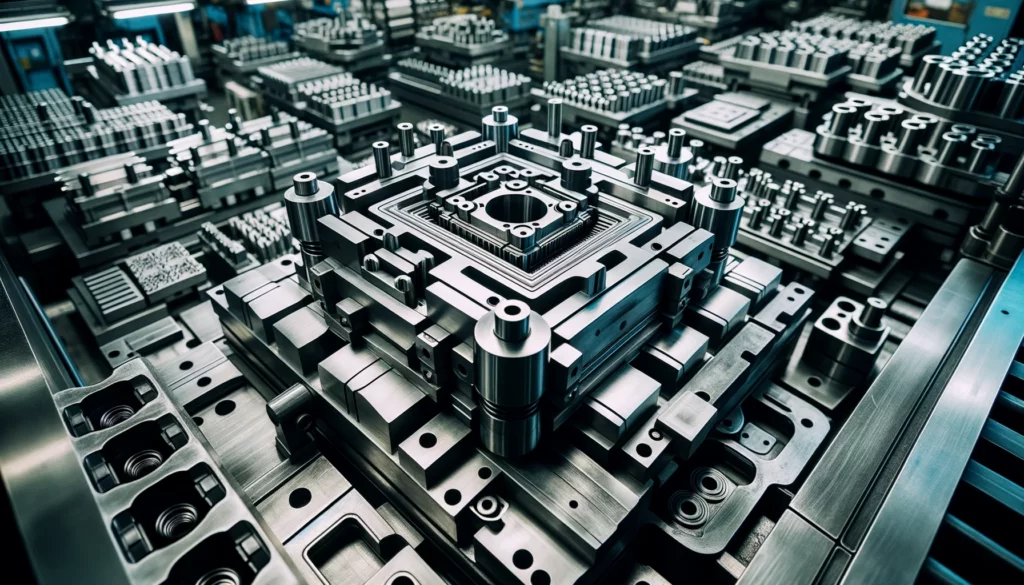
Stamping Die Manufacturing: Bringing Designs to Life (10-14 Days)
Transitioning from the abstract realm of design to the tangible domain of manufacturing is a pivotal leap in the process of creating precision micro stamped parts. The Stamping Die Manufacturing phase, spanning 10 to 14 days, is the crucible where the meticulously crafted designs are brought to life. It’s a stage marked by precision, technical expertise, and a keen eye for quality. Here’s a closer look at the key stages that unfold during this critical phase:
Preparing the Workshop:
Before the manufacturing begins, the workshop is prepared to ensure it’s equipped with the necessary machinery, materials, and other resources required for the task ahead. This preparation sets the stage for a smooth manufacturing process.
Material Procurement:
Procuring the right materials as specified during the design phase is crucial. The quality of materials directly impacts the quality and functionality of the stamping dies, underscoring the importance of this step.
Machining and Fabrication:
With materials in hand, the machining and fabrication process kicks off. Utilizing a blend of cutting-edge machinery and seasoned craftsmanship, the designs are translated into physical stamping dies. Each cut, each weld, and each assembly is carried out with a level of precision that mirrors the meticulousness of the design phase.
Quality Inspection:
As the stamping dies take shape, they are subjected to rigorous quality inspections. These inspections ensure that the manufacturing process is adhering to the specified tolerances and quality standards, ensuring a high level of precision and functionality.
Adjustments and Fine-Tuning:
Following inspection feedback, adjustments to the stamping dies are made as needed. This fine-tuning is critical to prepare the dies for subsequent testing and mass production stages.
Assembly:
After crafting, inspecting, and refining the components, they are meticulously assembled to create the full stamping die. This precise assembly is crucial for the die’s functionality and productivity.
Final Inspection and Documentation:
Post-assembly, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that the stamping dies are in perfect order and ready for the testing phase. Additionally, comprehensive documentation is prepared detailing the manufacturing process, the materials used, and other critical information that will be referenced in the subsequent phases.
Preparing for Testing:
With the stamping dies ready, preparations are made to transition to the First Off Tool (FOT) Sample phase. This includes ensuring that the testing environment is set up and ready to assess the performance of the newly manufactured stamping dies.
The Stamping Die Manufacturing phase is a testament to the meticulous planning and design that precedes it. It’s a phase where the abstract designs morph into tangible assets, ready to be tested and eventually, mass-produced. The essence of precision micro stamping lies in the flawless execution of this phase, setting the stage for the journey ahead towards creating high-quality micro stamped parts.

FOT Sample: The Testing Ground (3-7 Days)
The transition from design and manufacturing to the realm of testing is a decisive moment in the life cycle of precision micro stamped parts. The First Off Tool (FOT) Sample phase, spanning 3 to 7 days, is the arena where the stamping dies are put to the test, quite literally. This phase is the litmus test for all the meticulous planning, designing, and manufacturing that has transpired thus far. Let’s delve into the intricate steps that characterize this crucial phase:
Preparation:
Before the testing can commence, a conducive environment is prepared. This includes setting up the testing apparatus, ensuring the availability of necessary tools, and creating a schedule for the testing process. Preparation is key to ensure a seamless testing phase.
Initial Production Run:
The newly manufactured stamping dies are put to work in an initial production run to create the first batch of micro stamped parts. This initial run is a precursor to the testing process, providing the first glimpse of how the designs translate to actual products.
Sample Collection:
From the initial production run, samples are collected for a comprehensive evaluation. These samples are the representatives of the entire batch and hence are chosen with care to ensure they embody the characteristics of the overall production.
Dimensional Analysis:
The collected samples undergo a rigorous dimensional analysis to ensure they adhere to the specified tolerances and dimensions. Precision is the name of the game, and this analysis is pivotal to ensure the micro stamped parts meet the stringent quality standards.
Material Testing:
The material properties of the samples are tested to ensure they align with the specifications. This includes testing for hardness, tensile strength, and other material properties that are crucial for the functionality and durability of the micro stamped parts.
Functional Testing:
Beyond the dimensions and material properties, the samples are subjected to functional testing to assess their performance in real-world conditions. This testing is tailored to mimic the conditions the parts will face in their operational environment.
Feedback and Adjustments:
Based on the testing results, feedback is provided to the manufacturing team. If any discrepancies are found, necessary adjustments are made to the stamping dies to rectify the issues.
Re-testing (if necessary):
In case adjustments are made, a re-testing process is conducted to ensure the issues have been rectified and the samples now adhere to the specifications and quality standards.
Documentation and Approval:
The results of the testing phase are meticulously documented, providing a detailed account of the findings. Upon successful testing, the FOT samples are approved, paving the way for the mass production phase.
Transition to Mass Production:
With the approval of the FOT samples, preparations are initiated to transition to the Mass Production phase. The successful culmination of the FOT Sample phase is a green signal that the project is on the right track, ready to shift gears to mass production.
The FOT Sample phase is a blend of anticipation and meticulous evaluation, ensuring that the micro stamped parts are ready to meet the demands of mass production. It’s a phase that underscores the importance of quality and precision, hallmarks of a successful precision micro stamping project.

Mass Production: The Manufacturing Marathon (20-30 Days)
The crescendo of the precision micro stamped parts project is undoubtedly the Mass Production phase, a marathon that spans 20 to 30 days. This is the arena where the approved designs and tested stamping dies prove their mettle, as they are tasked with producing high-quality parts en masse to meet market demands. Every preceding phase converges at this juncture, as the production floor buzzes with the rhythm of manufacturing. Here’s a glimpse into the meticulous steps and processes that characterize this extensive phase:
Pre-production Meeting:
Before the machines roar to life, a pre-production meeting is convened. Here, the teams involved review the project requirements, the approved designs, and the insights gained from the FOT Sample phase. This meeting ensures everyone is on the same page as they step into the mass production phase.
Setting Up Production Lines:
The production lines are set up, aligning with the specifics of the project. The stamping dies are installed, machinery calibrated, and the necessary materials sourced and organized. This setup is crucial for a smooth, efficient production process.
Pilot Production Run:
Before full-scale production commences, a pilot production run is conducted. This run serves as a final check to ensure the production line is ready for mass production. Any last-minute adjustments or calibrations are made during this phase.
Ramp-up to Full-Scale Production:
With the successful completion of the pilot run, the production line ramps up to full-scale production. The machinery hums in a synchronized dance as the micro stamped parts are produced at scale.
Continuous Quality Monitoring:
Quality is not a one-off check but a continuous process. As production progresses, continuous quality monitoring is conducted to ensure the micro stamped parts adhere to the specified tolerances and quality standards.
Process Optimization:
Simultaneously, efforts are directed towards process optimization to enhance efficiency and productivity. This could involve tweaking machine settings, reorganizing workflow, or other measures to ensure optimum production output.
Packaging and Labeling:
As the micro stamped parts roll off the production line, they are packaged and labeled as per the project requirements. This phase also includes a final quality check before the products are sent off to the packaging department.
Documentation and Reporting:
Comprehensive documentation is maintained, capturing the details of the production process, quality control measures, and other relevant information. Regular reports are generated to provide insights into the production progress and quality metrics.
Preparing for Dispatch:
With production complete, the products are prepared for dispatch. This includes organizing the logistics, ensuring the products are securely packaged, and all necessary documentation is in place for a smooth transit to the destination.
Transition to Booking and Shipping Phase:
As the Mass Production phase winds down, preparations are initiated to transition to the Booking and Shipping phase. This marks the end of the manufacturing marathon and the beginning of the journey of the micro stamped parts to their respective destinations.
The Mass Production phase is a testament to the meticulous planning, designing, and testing that precede it. It’s a phase characterized by a blend of precision, efficiency, and the relentless pursuit of quality. As the micro stamped parts are churned out, ready to serve their purpose, the project inches closer to the finish line, echoing the meticulousness and precision that is the hallmark of precision micro stamping.

Booking & Shipping: The Final Lap (7-10 Days)
As the marathon of precision micro stamping project approaches its finish line, the Booking and Shipping phase marks the final lap. Spanning 7 to 10 days, this phase transitions the meticulously manufactured parts from the production floor to their destined locations across the globe. The euphoria of successful manufacturing now blends with the anticipation of delivering these products into the hands of awaiting clients. Let’s navigate through the key steps and elements that define this concluding phase:
Inventory Check and Final Inspection:
Before the products embark on their journey, a final inventory check is conducted to ensure all the manufactured parts are accounted for and aligned with the order specifications. A final inspection for quality and accuracy is also carried out to ensure that only top-notch products are dispatched.
Booking Logistics:
The logistics for shipping the products are booked during this phase. This involves selecting reliable logistics partners, scheduling pickups and deliveries, and ensuring all the necessary paperwork is in order for a smooth transit.
Packaging for Transit:
A critical aspect of this phase is ensuring the products are securely packaged for transit. The packaging is designed to protect the micro stamped parts from any damage during transportation, ensuring they reach the client in pristine condition.
Documentation and Customs Compliance:
Ensuring compliance with shipping and customs regulations is paramount. All the necessary documentation, including shipping manifests, invoices, and customs paperwork, is prepared and double-checked for accuracy to avoid any delays or issues during transit.
Tracking and Communication:
Once the products are on their way, tracking information is generated and communicated to the clients. Regular updates on the shipping status keep the clients informed and build trust in the process.
Transit Insurance:
To mitigate the risks associated with transit, insurance coverage is arranged for the shipment. This provides a safety net against any unforeseen events that might occur during transportation.
Receiving and Confirmation:
Upon arrival at the destined locations, the shipments are received and inspected by the clients. Any discrepancies are reported, and necessary actions are taken to resolve them.
Feedback Collection:
Feedback from the clients regarding the quality of the products and the overall experience is collected. This feedback is invaluable for continuous improvement and building long-term relationships with the clients.
Closing the Project:
With the successful delivery of the products, the project is officially closed. A final review is conducted to evaluate the performance across all phases of the project, and lessons learned are documented for future reference.
Preparation for Future Orders:
Even as one project concludes, preparations for future orders may already be underway. The insights gained from the completed project are utilized to enhance the processes for upcoming projects.
The Booking and Shipping phase encapsulates the culmination of a well-orchestrated project, marking the end of one journey and the potential beginning of another. It’s a phase that underscores the meticulous attention to detail and customer-centric approach that is characteristic of a successful precision micro stamping venture, ensuring not just the creation of high-quality micro stamped parts, but their safe and timely delivery to the awaiting hands of clients, ready to serve their destined purpose in the myriad applications they were crafted for.
Conclusion
Understanding the lead time for precision micro stamped parts is crucial for setting realistic project timelines and ensuring seamless coordination between all involved parties. Each phase, from initial communication to the final shipping, holds its significance, cumulatively contributing to the overall lead time, ensuring the delivery of precision-engineered, quality micro stamped parts.



